| Version 8 (modified by , 8 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
NUISCOMP
The NUISANCE comparison application can be used to generate MC predictions that can be directly compared with published scatter data by automatically selecting the correct event topologies from a provided event sample and binning them to match the data.
Wiki content
Running NUISCOMP
Author: Patrick Stowell
Date: June 2017
Versions: NUISANCE v2r0, GENIE 2.12.6
The following example details how to run NUISANCE and produce MiniBooNE pion production comparisons to a generator of choice. Each generator requires very slightly different ways to handle NUISANCE, therefore multiple versions of this tutorial have been provided. Please use the following links to choose what generator you would like to use.
Generating GENIE Events
If we want to see how a given GENIE model behaves, first we need to generate events. This can be done using the standard gevgen application, using the appropriate target and flux for a given data sample.
If all you want to do is check your NUSIANCE is built correctly, you can skip this step by downloading MC files from our online storage area by following the steps found here:LinkToNUISANCEMCFiles
Running gevgen
The standard gevgen application options can be ran using
$ gevgen -f -n -e
We need to provide a flux and target list to GENIE when running gevgen. To see our list of compiled flux and target combinations for each sample please see here:
Note: If building NUISANCE v2r0 or higher against GENIE 2-12-0 or higher an option is provided to use an easier and quicker gevgen_nuisance application to generate NUISANCE-ready event files. Please see section 2.3 if you would like to use this.
We want to run comparisons to MiniBooNE muon-neutrino scattering data on a mineral oil target, therefore to generate events we can run
$ gevgen -f MiniBooNE -t CH
Once our events have been generated we can check that they have finished correctly by opening the output event file has a ‘gtree’ object and the flux spectrum file contains the correct histogram.
$ root gntp.2063030.ghep.root root [0] Attaching file gntp.2063030.ghep.root as _file0... Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::NtpMCEventRecord is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::NtpMCRecordI is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::NtpMCRecHeader is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::EventRecord is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::GHepRecord is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::Interaction is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::InitialState is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::Target is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::ProcessInfo is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::Kinematics is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::XclsTag is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::KPhaseSpace is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class genie::GHepParticle is available Warning in <TClass::TClass>: no dictionary for class pair<genie::EKineVar,double> is available root [1] _file0->ls(); TFile** gntp.2063030.ghep.root TFile* gntp.2063030.ghep.root KEY: genie::NtpMCTreeHeader header;1 GENIE output tree header KEY: TFolder gconfig;1 GENIE configs KEY: TFolder genv;1 GENIE user environment KEY: TTree gtree;1 GENIE MC Truth TTree, Format: [NtpMCEventRecord]
$ root input-flux.root root [0] Attaching file input-flux.root as _file0... root [1] _file0->ls(); TFile** input-flux.root TFile* input-flux.root KEY: TH1D spectrum;1 neutrino_flux
Now that the event samples have been generated correctly, we need to prepare them for use in NUISANCE.
Running PrepareGENIE
The standard gevgen application doesn’t save the total event rate predictions into the event file itself. NUISANCE needs these to correctly normalise predictions so before we can use these new events we need to prepare them.
The PrepareGENIE application is built when NUISANCE is built with GENIE support should be available after the NUISANCE environmental setup script is ran.
$ PrepareGENIE -h
PrepareGENIEEvents NUISANCE app.
Takes GHep Outputs and prepares events for NUISANCE.
PrepareGENIEEvents [-h,-help,--h,--help]
[-i inputfile1.root,inputfile2.root,inputfile3.root,...]
[-f flux_root_file.root,flux_hist_name]
[-t target1[frac1],target2[frac2],...]
Prepare Mode [Default] : Takes a single GHep file, reconstructs the original GENIE splines, and creates a duplicate file that
also contains the flux, event rate, and xsec predictions that NUISANCE needs.
Following options are required for Prepare Mode:
[ -i inputfile.root ] : Reads in a single GHep input file that needs the xsec calculation ran on it.
[ -f flux_file.root,hist_name ] : Path to root file containing the flux histogram the GHep records were generated with. A
simple method is to point this to the flux histogram genie generatrs '-f /path/to/events/input-flux.root,spectrum'.
[ -t target ] : Target that GHepRecords were generated with. Comma seperated list. E.g. for CH2
target=1000060120,1000010010,1000010010
The PrepareGENIE application, when ran, loops over all the events, extracts the cross-section as a function of energy for each discrete interaction mode and uses this information to reconstruct the cross-section splines for each target that were used to generate events.
These splines are then multiplied by specified flux and added according to the target definition provided to produce total flux and event rate predictions as a function of energy for the sample and saves them into the events file.
We want to prepare our MiniBooNE events so we pass in the event files, the input flux, and the CH2 target definition.
$ PrepareGENIE -i gntp.2063030.ghep.root -f input-flux.root,spectrum -t 1000060120,1000010010,1000010010
Now when we open our event file again, we should see the flux and event rate histograms are now saved into the file ready for NUISANCE to read them.
KEY: genie::NtpMCTreeHeader header;1 GENIE output tree header KEY: TFolder gconfig;1 GENIE configs KEY: TFolder genv;1 GENIE user environment KEY: TTree gtree;1 GENIE MC Truth TTree, Format: [NtpMCEventRecord] KEY: TDirectoryFile IndividualGENIESplines;1 IndividualGENIESplines KEY: TDirectoryFile TargetGENIESplines;1 TargetGENIESplines KEY: TH1F nuisance_xsec;1 KEY: TH1F nuisance_events;1 KEY: TH1F nuisance_flux;1
Running gevgen_nuisance (optional)
Other than the standard gevgen application, if built against GENIE events later than GENIE 2.12.0, NUISANCE can also provide a gevgen_nuisance app, with additional features to support the creation of ‘NUISANCE-ready’ events.
To build gevgen_nuisance, you will need to build with the option ‘-DBUILD_GEVGEN=ON’ during the cmake configure statement as shown in the build notes here:
$ cmake ../ -DUSE_GENIE=1 -DBUILD_GEVGEN=1
The gevgen_nuisance can be ran in a similar way to the normal gevgen application but flux inputs and target definitions can be provided in simpler formats
In our example we want to generate events for a MiniBooNE muon neutrino flux on a CH2 target. Therefore we run
$ gevgen_nuisance -n 250000 -f MiniBooNE_fhc_numu -t CH2
We should then open the output event file to check it constrains the GENIE event tree ‘gtree’ object and the flux and event rate predictions.
Notice that we no longer need to run PrepareGENIE on gevgen_nuisance events before using them nuisance.
gevgen_nuisance also provides extra support for mixed target and flux specifications. For further notes on these see:
Setting up a GENIE Comparison
Now that we have an event sample we can load them load them into NUISANCE by specifying them at run time. To do that we need to write a NUISANCE card file that lists all comparisons that should be made and the event files that should be used for each one.
We want to produce comparisons to MiniBooNE pion production data, so first we should search the NUISANCE sample list.
The ‘nuissamples’ script is provided for easy access of the sample list. Running it without any arguments will return a full sample list of available data comparisons. Providing an additional argument will return only samples containing the provided substring.
We can list the MIniBooNE samples using
[stowell@hepgw1 ~]$ nuissamples MiniBooNE MiniBooNE_CCQE_XSec_1DQ2_nu MiniBooNE_CCQELike_XSec_1DQ2_nu MiniBooNE_CCQE_XSec_1DQ2_antinu MiniBooNE_CCQELike_XSec_1DQ2_antinu MiniBooNE_CCQE_CTarg_XSec_1DQ2_antinu MiniBooNE_CCQE_XSec_2DTcos_nu MiniBooNE_CCQELike_XSec_2DTcos_nu MiniBooNE_CCQE_XSec_2DTcos_antinu MiniBooNE_CCQELike_XSec_2DTcos_antinu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DEnu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DQ2_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_2DQ2Enu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_2DTpiCospi_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_2DTpiEnu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_2DTuCosmu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_2DTuEnu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pi0_XSec_1DEnu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pi0_XSec_1DQ2_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pi0_XSec_1DTu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pi0_XSec_1Dcosmu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pi0_XSec_1Dcospi0_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pi0_XSec_1Dppi0_nu MiniBooNE_NC1pi0_XSec_1Dcospi0_antinu MiniBooNE_NC1pi0_XSec_1Dcospi0_rhc MiniBooNE_NC1pi0_XSec_1Dcospi0_nu MiniBooNE_NC1pi0_XSec_1Dcospi0_fhc MiniBooNE_NC1pi0_XSec_1Dppi0_antinu MiniBooNE_NC1pi0_XSec_1Dppi0_rhc MiniBooNE_NC1pi0_XSec_1Dppi0_nu MiniBooNE_NC1pi0_XSec_1Dppi0_fhc MiniBooNE_NCEL_XSec_Treco_nu
We only care about CC1pip data therefore the following samples are of interest
[stowell@hepgw1 ~]$ nuissamples MiniBooNE_CC1pip MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DEnu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DQ2_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_2DQ2Enu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_2DTpiCospi_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_2DTpiEnu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_2DTuCosmu_nu MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_2DTuEnu_nu
In this example we will compare to the 1Dtpi and 1DTu distributions, but we could provide any number of the samples seen in the lists.
We write our card file with these two datasets using the following sample object format:
sample NAME_OF_SAMPLE INPUT_TYPE:FILE_INPUT
So for our genie files generated in step 2.1, our card file would be :
genie_tutorial.card
sample MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu GENIE: gntp.2063030.ghep.root sample MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTu_nu GENIE: gntp.2063030.ghep.root
We can now run our cardfile using the standard nuisance application like so:
$ nuiscomp -c genie_tutorial.card -o genie_samples.root
In total this will produce a lot of logging output, so only some snippets are included below for comparison.
[LOG Fitter]: Starting nuiscomp.exe ... [LOG Minmzr]:- Loading Sample : MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu [LOG Sample]:-- Loading Sample : MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu [LOG Sample]:-- Creating GENIEInputHandler : MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu |-> Total Entries : 2500000 |-> Event Integral : 1.47491e-28 events/nucleon |-> Flux Integral : 1.67753e+10 /cm2 |-> Event/Flux : 8.79217e-39 cm2/nucleon ... [LOG Fitter]: Generating Comparison. [LOG Reconf]:--- Starting Reconfigure iter. 0 [LOG Reconf]:--- Event Manager Reconfigure [LOG Reconf]:--- MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu : Processed 0 events. [M, W] = [33, 1] [LOG Reconf]:--- MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu : Processed 500000 events. [M, W] = [13, 1] ... [LOG Fitter]: Saving current full FCN predictions [LOG Minmzr]:- Writing each of the data classes... [LOG Sample]:-- Written Histograms: MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu [LOG Sample]:-- Written Histograms: MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTu_nu [LOG Fitter]: ------------------------------------ - [LOG Fitter]: Comparison Complete. [LOG Fitter]: ------------------------------------ -
To check that the comparison definitely finished successfully, lets open the root file and check the file is not empty.
$ root genie_allsamples.root Attaching file genie_allsamples.root as _file0... root [0] TBrowser b
If you see something similar to this then the comparisons should have ran successfully.
Analysing the output
When we open the NUISANCE output file in ROOT we can see that it contains a series of histograms all with names similar to the sample names we specified in our card file. By default NUISANCE preppends the name of the sample to any histogram when writing it so that you know from what sample each histogram originated from.
Lets go through some of the histograms of interest.
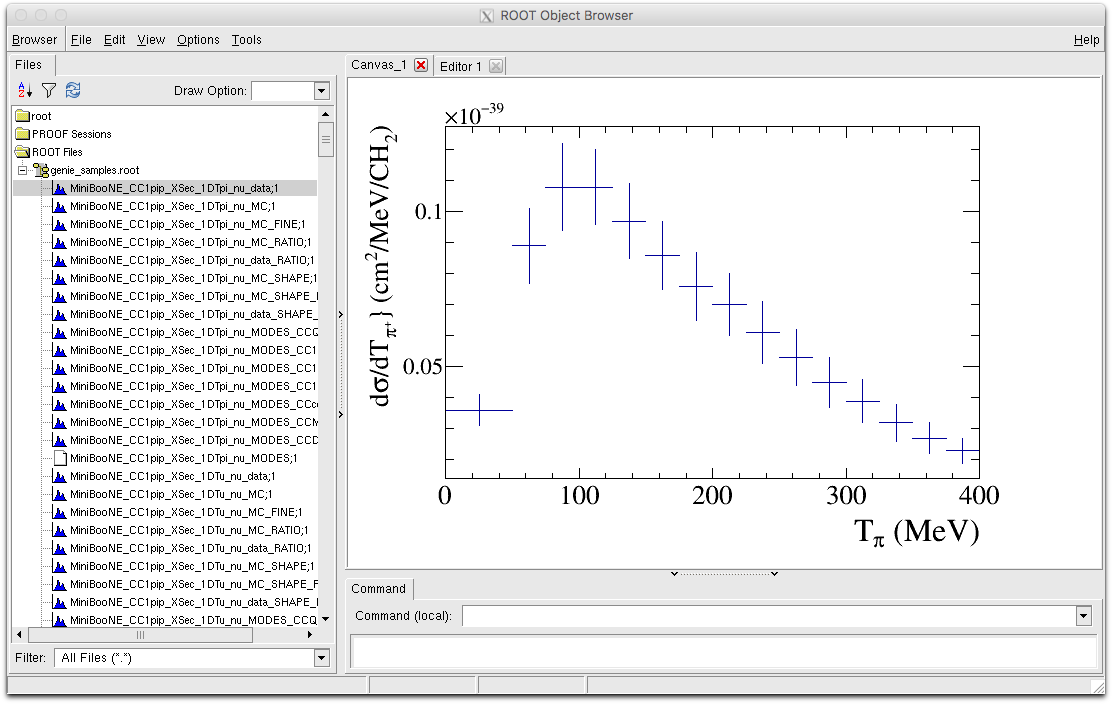
- MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu_data : This is the data histogram we are trying to compare to for the Tpi distribution. Drawing this with the ROOT draw option 'E1' will draw us the error bands.
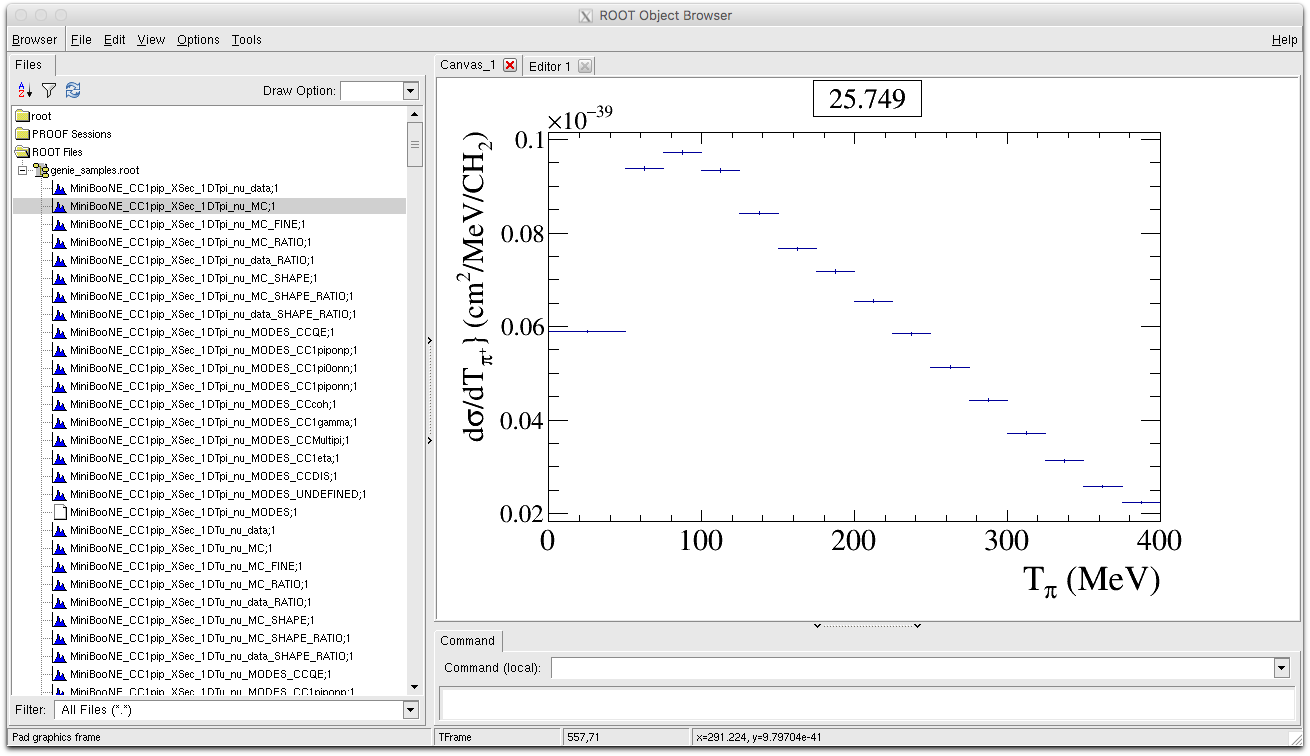
- MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu_MC : This is the MC histogram for our model binned in exactly the same binning as the data. Error bars attached to the MC histogram are defined as the statistical error in each bin given your MC event sample. This histogram is also used to calculate a likelihood by directly comparing to the data. By default the title of the MC histogram is also set to the value of the likelihood for easy reference. In the plot below the chi2 was calculated to be : 25.749.
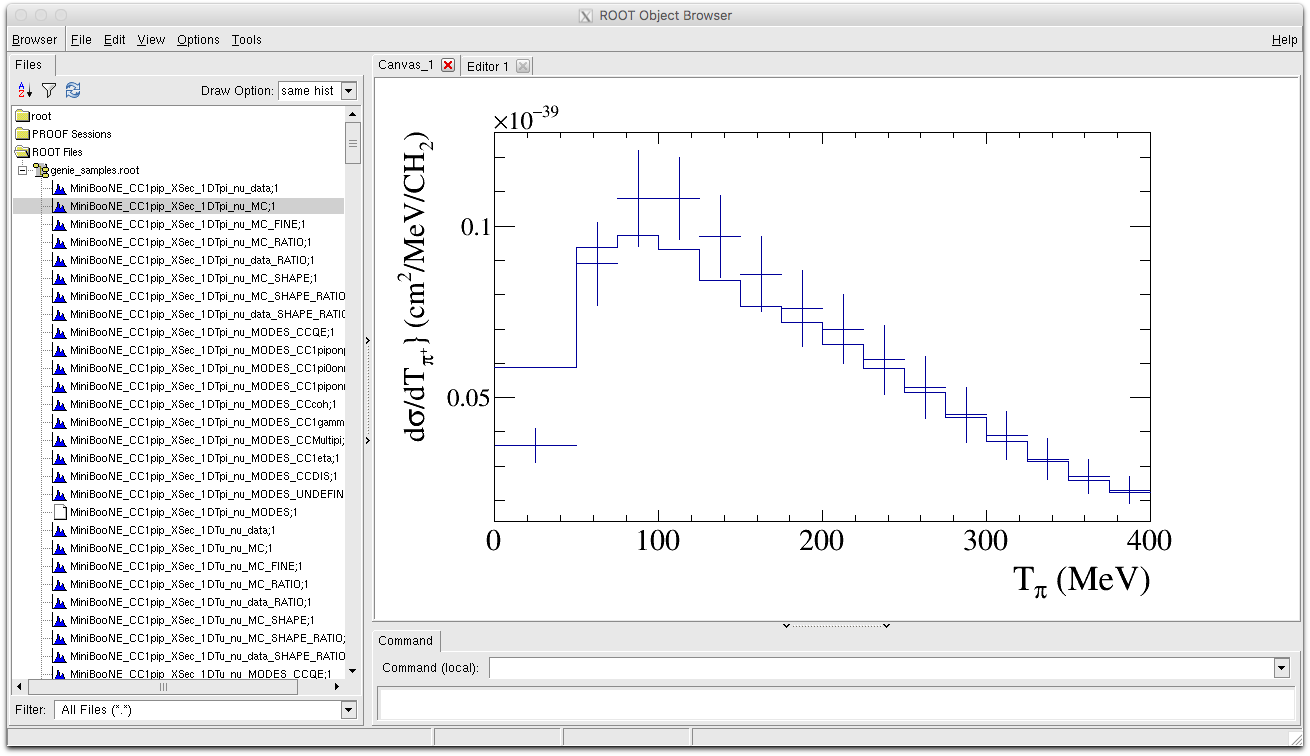
We can also directly compare the MC and data histograms, by drawing the data with the option 'E1' then drawing the MC histogram with the option "HIST SAME".
Providing reweight parameters
The comparisons application also allows different GENIE reweight parameters to be provided in our card file.
The format for this is:
genie_parameter NAME VALUE STATE
- NAME : Specifies the name of the reweight dial. These can be found in '$GENIE/src/ReWeight/GSyst.cxx'
- VALUE: Value of the reweight dial in units of 1-sigma variations (1-sigma defined by GENIE)
- STATE: State of this parameter dial, for most cases this should be left as 'FIX'.
In our example we shall generate another set of comparisons this time with two parameters shifted.
- Charged Current Resonant Axial Mass : Axial mass parameter used in the resonant form factor
- Charged Current Resonant Normalisation : Total normalisation of CCRES events.
First we look for the possible name in GENIE reweight:
$GENIE/src/ReWeight/GSyst.h
class GSyst {
public:
//......................................................................................
static string AsString(GSyst_t syst)
{
switch(syst) {
case ( kXSecTwkDial_MaNCEL ) : return "MaNCEL"; break;
...
case ( kXSecTwkDial_NormCCRES ) : return "NormCCRES"; break;
case ( kXSecTwkDial_MaCCRESshape ) : return "MaCCRESshape"; break;
case ( kXSecTwkDial_MvCCRESshape ) : return "MvCCRESshape"; break;
case ( kXSecTwkDial_MaCCRES ) : return "MaCCRES"; break;
case ( kXSecTwkDial_MvCCRES ) : return "MvCCRES"; break;
We can see the dials we are interested in this list, specified by the strings: 'MaCCRES' and 'NormCCRES' respectively.
Now we want to change these dials to +1 for MaCCES and -1 sigma for NormCCRES. Therefore we add the following lines to our card file:
genie_parameter MaCCRES +1.0 FIX genie_parameter NormCCRES -1.0 FIX
so that it now looks like the following
genie_tutorial.card
genie_parameter MaCCRES +1.0 FIX genie_parameter NormCCRES -1.0 FIX sample MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu GENIE: gntp.2063030.ghep.root sample MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTu_nu GENIE: gntp.2063030.ghep.root
With this new card file we can then run our comparisons again, but this time save the output to a different file
$ nuiscomp -c genie_tutorial.card -o genie_samples_reweighted.root [LOG Fitter]: Starting nuiscomp.exe ... [LOG Fitter]: Setting up nuiscomp [LOG Fitter]: Number of parameters : 2 [LOG Fitter]: Read genie_parameter : MaCCRES = 1 : [LOG Fitter]: Read genie_parameter : NormCCRES = -1 : ... [LOG Fitter]: Setting up FitWeight Engine [LOG Fitter]: Registed Dial Enum : MaCCRES 5 5011 [LOG Fitter]: Setting up GENIE RW : genierw ... [LOG Reconf]:--- Starting Reconfigure iter. 0 [LOG Reconf]:--- Event Manager Reconfigure [LOG Reconf]:--- MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu : Processed 0 events. [M, W] = [33, 1] [LOG Reconf]:--- MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu : Processed 500000 events. [M, W] = [13, 1] [LOG Reconf]:--- MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu : Processed 1000000 events. [M, W] = [13, 1] [LOG Reconf]:--- MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu : Processed 1500000 events. [M, W] = [11, 1.17986] [LOG Reconf]:--- MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu : Processed 2000000 events. [M, W] = [51, 1] ... [LOG Minmzr]:- Writing each of the data classes... [LOG Sample]:-- Written Histograms: MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu [LOG Sample]:-- Written Histograms: MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTu_nu [LOG Fitter]: ------------------------------------ - [LOG Fitter]: Comparison Complete. [LOG Fitter]: ------------------------------------ -
You might have noticed that now during the event processing stage, the values [M, W] correspond to the [Mode, Weight] for the event processed at that point, and that now we have added reweight dials, the weights are not always equal to 1.0.
Now lets open up both our comparison files and compare the outputs
$ root genie_samples.root genie_samples_reweighted.root root [2] TBrowser b
We now have two files with the exact same structure, the only differences between these will be the values given in each of the MC histograms.
If we compare the MiniBooNE_CC1pip_XSec_1DTpi_nu_MC histograms on a single plot against the data we can see that the normalisation of the reweighed prediction has shifted upwards, and the likelihood for that prediction given the data has gotten worse as a result.
Attachments (8)
- screenshot.png (80.6 KB) - added by 8 years ago.
- screenshot_1.png (78.9 KB) - added by 8 years ago.
- screenshot_3.png (75.3 KB) - added by 8 years ago.
- screenshot_2.png (83.4 KB) - added by 8 years ago.
- screenshot_5.png (68.7 KB) - added by 8 years ago.
- screenshot_8.png (79.5 KB) - added by 8 years ago.
- screenshot_6.png (79.7 KB) - added by 8 years ago.
- screenshot_7.png (75.7 KB) - added by 8 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip